
Phobias, classified as specific phobias in the realm of anxiety disorders, are characterized by excessive and irrational fears of specific objects, situations, or activities.
While experiencing fear is a natural response to perceived threats, phobias involve an exaggerated and persistent dread that can interfere significantly with daily functioning. In adulthood, individuals may struggle with a variety of common phobias, each with its distinct triggers and manifestations, ranging from fears of specific stimuli to broader social anxieties.
These phobias can exert a profound impact on various aspects of adult life, affecting relationships, career opportunities, and overall well-being.
Recognizing the prevalence and effects of these common phobias is crucial for fostering understanding and support among individuals navigating these challenges. In what follows, we’ll discuss some of the most prevalent types of phobias encountered by adults and their general implications.
Four Common Phobias
Common phobias in adults encompass a range of fears and anxieties that can significantly impact daily life and well-being.
Social phobia, agoraphobia, arachnophobia, and claustrophobia are among the most prevalent types of phobias encountered by adults, each with its unique triggers and manifestations.
Social Phobia/Social Anxiety Disorder
Social phobia, also known as social anxiety disorder (SAD), is characterized by an intense fear of social situations where individuals fear judgment, embarrassment, or scrutiny by others.
Adults with social phobia may avoid social interactions, public speaking, or situations where they feel exposed or vulnerable. The fear of being negatively evaluated can lead to significant distress and impairment in social, occupational, and academic settings.
Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia involves a fear of situations or places where escape may be difficult or embarrassing, leading to feelings of helplessness or entrapment.
Adults with agoraphobia may avoid crowded places, public transportation, or unfamiliar environments, fearing panic attacks or loss of control. Agoraphobia can severely limit a person’s ability to engage in daily activities and may lead to social isolation or dependence on others for support.
Arachnophobia
Arachnophobia is one of the most common specific phobias, characterized by an intense and irrational fear of spiders.
Adults with arachnophobia may experience panic attacks, avoidance behaviors, or extreme distress when encountering spiders or even thinking about them. This fear may be rooted in evolutionary factors, cultural influences, or personal experiences.
Claustrophobia
Claustrophobia involves a fear of enclosed or confined spaces, such as elevators, tunnels, or crowded rooms, where escape may be difficult or restricted. Adults with claustrophobia may experience panic attacks, shortness of breath, or intense feelings of dread when in enclosed spaces.
This fear may stem from past traumatic experiences, such as being trapped or confined or a general sense of vulnerability in enclosed environments.
While phobias can be debilitating, effective treatment options, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and medication, can help individuals manage symptoms and regain control over their lives.

Treatment Options for Phobias
Addressing common phobias in adults involves a variety of treatment options aimed at reducing anxiety symptoms, overcoming fears, and improving overall well-being. Here are some effective approaches to managing phobias:
Self-help and Support Groups
Self-help techniques, such as relaxation exercises, mindfulness meditation, and gradual exposure to feared situations, can be beneficial for individuals with common phobias.
Joining support groups or online communities allows individuals to connect with others facing similar challenges, share experiences, and receive encouragement and advice in a supportive environment.
Medication
Medication may be prescribed to alleviate anxiety symptoms associated with common phobias, particularly for individuals with severe or debilitating anxiety. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as sertraline (Zoloft) or fluoxetine (Prozac), are commonly prescribed antidepressants that can help reduce anxiety symptoms over time.
Beta-blockers, such as propranolol, may also be prescribed to manage physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat or trembling, in specific situations, such as public speaking or performance anxiety.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is a behavioral therapy technique commonly used to treat phobias by gradually exposing individuals to feared stimuli or situations in a controlled and systematic manner.
Through repeated exposure and relaxation techniques, individuals learn to confront their fears, reduce anxiety responses, and develop coping skills to manage anxiety effectively.
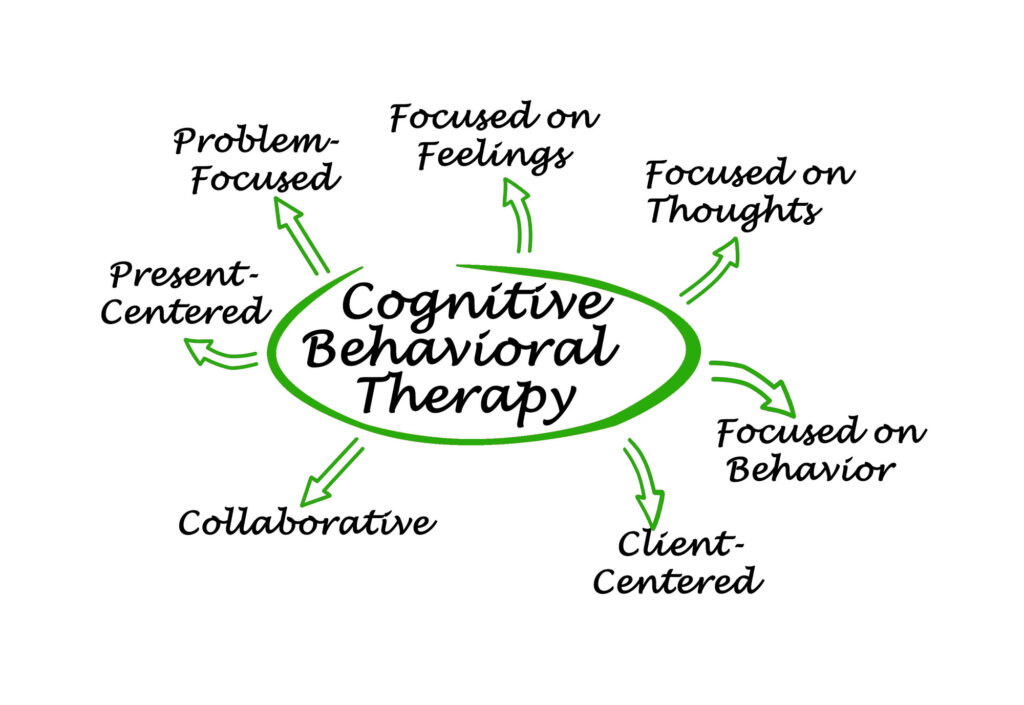
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a highly effective treatment approach for common phobias in adults.
CBT focuses on identifying and challenging irrational thoughts and beliefs associated with phobic fears, learning coping skills and relaxation techniques to manage anxiety symptoms, and gradually exposing individuals to feared situations to desensitize them to anxiety triggers.
Final Thoughts
Effective treatment options for common phobias in adults include self-help techniques, support groups, medication, exposure therapy, and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
By utilizing these approaches in combination or individually, individuals with phobias can learn to manage their anxiety symptoms, confront their fears, and regain control over their lives. Seeking professional help from qualified mental health professionals is essential for developing personalized treatment plans and receiving guidance and support throughout the recovery process.
This content was written and reviewed by a medical doctor. 
Mental Health Issues in Seniors
As individuals age, they may face various mental health challenges that can significantly impact their overall well-being.
From Flirting to Hurting: The Ugly Truth About Negging
Negging is more than just an offhand remark; it’s a calculated move designed to undermine your confidence while appearing friendly.
Suicide Prevention and Awareness
Suicide is a global public health issue that affects individuals, families, and communities worldwide. Despite its prevalence, it remains a topic shrouded in stigma and silence.
Veterans’ Mental Health
Overview The mental health challenges faced by veterans often stem from a combination of factors unique to their military service experiences and post-deployment transition to civilian life.




